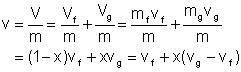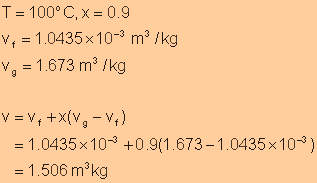Tables in SI units start from page 897 (Appendix 1).
Tables in English units start from page 947 (Appendix 2).
|
Table
A-4
|
pp.
904-905
|
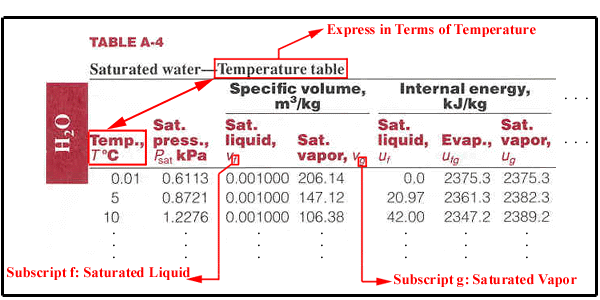
Saturated Water: Temperature Table | |
|
Table
A-5
|
pp.
906-907
|
Saturated Water: Pressure Table |
 |
||
|
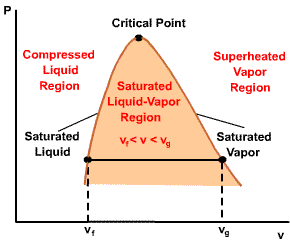
The total volume of the liquid-vapor mixture can be determined as follows:
|
||||||||||
|
 |
|||
|
Table
A-6
|
pp.
908-911
|
Superheated Water | |
|
Table
A-7
|
pp.
912
|
Compressed Liquid Water |
In the superheated vapor table, the values begin with the saturated vapor state. The data in the compressed liquid table end with saturated liquid states.
Linear interpolation is required when the states encountered in problems do not fall exactly on the values provided by the tables.
|
Enthalpy
(H) |
H = U + pV | ||
| Specific Enthalpy (h) | h = u + pv | ||
| Specific Internal Energy (u) | |||
|
Exercise
|
 |
Go to the Thermodynamics
Tables Wizard for the workshops.
The values of u, h, and s given in the property tables are not obtained
by direct measurement but are calculated from other data that can be more
readily determined experimentally.
When applying the energy analysis, it is the difference in internal, kinetic and potential energy between two states that are important, and not the values of these energy quantities themselves.
The reference value cancels as long as the calculations being performed involve only differences in these properties.
Water
Reference state: triple point
Reference value: ![]() (
(![]() )
)